Pleasure of Iso Fukase Fishing
Have you heard about Iso fishing before?
Iso stands for rocky coast in Japanese. For Japanese anglers, Iso is the place with rich target fish, which are not commercially available but very tasty. You can say that Iso is an angling paradise, because only anglers are interested in Iso and that it is untouched by non-angler people. There are two traditional styles of Iso fishing, Fukase and Sokomono. Fukase is float fishing with chumming, and Sokomoto is to fish for bottom feeders with cast-and-wait style. In this article, I would like to introduce Fukase style Iso fishing. Its concept is simple, but, as is often the case in any styles of fishing, things are not straightforward and this makes the game fun.
Geographic information of Iso in Japan
Around Japan, the total length of coastline is 32,799 km. Out of it, the natural shore length is 17,414 km. Hence, about 50% of the Japanese coastline is holding its natural condition. Among this natural coastline, about 23% is of rocky sea shore and it sums up to the length of nearly 4,000 km is Iso. (from the research report of Biodiversity Center of Japan)
These rocky coasts are often located at the place where steep mountains or hills are adjacent to the sea. Often, these are formed by the submergence of the land (not formed by glaciers), and it creates the complex coastline. This is called ria coast, under the terms of landform.
This rocky shore creates the complex flow of the sea water, especially at the place where the current strikes. It creates better conditions for various fish, because it brings fresh sea water full of nourishment, with many places for fish to hide. If you go deep inside of the naturally formed bay, there is calm water, in which baby fish can safely grow.
Target of Iso Fukase
Fukase angler’s favorite target is Mejina (or Gure in western Japan, Largescale blackfish, Girella Punctana Gray.) and Kurodai (or Chinu in western Japan, Blackhead seabream, Acanthopagrus schlegelii.) Comparing these two target species, Mejina lives in Iso facing the oceanic current, and Kurodai does in diverse areas.Hence, Kurodai is a more accessible fish. And, as for the Iso Fukase fishing, Mejina is what many people are dreaming of.
Mejina dwells in the middle of Honshu and further south western Japan. The most northern area where you can see the adults is Chiba and Niigata. It is omnivorous, and eats seaweeds or crustaceans, depending on the season. Early spring is the spawning season. It is said that winter is the best timing for fishing, because in winter its feeding is active and it tastes better.
Mejina moves around in school, and searches for food such as seaweed in winter, and small crustaceans in warm seasons.
Mejina grows up to 60 cm. Within its high body, it has a lot of muscles to swim in the strong water current around iso. It has immense pulling power when hooked, especially for downwards.
Iso Fukase fishing (Rocky shore float fishing)
Fukase is a float fishing with chumming. Fish are attracted by chumming and they mistakenly take bait with a hook, amid the cloud of chumming in the water, and get hooked. It is as simple as that.
The game of Fukase fishing starts when you think about the flow of the water, drifting chums and movements of the rig. How do you present your hook in the middle of flowing chums? It is the primary question.
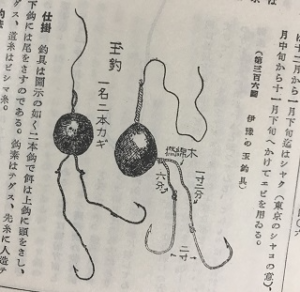
Fishing tackles for Iso Fukase
The tackle and rig is very simple. Float, small split shot sinker, leader and a hook.
Rod is 4.5 - 5.3 m, Iso Fukase special rod which has very soft tip and generally parabolic action. The rod action is a Japanese traditional action (please check traditional rod actions in another article of mine; Bamboo and Action of Japanese Fishing Rods.) It is long enough to cushion shocks on the line. Spinning reels, special lever brake type reels, are used.
This lever brake works to control the backwinding of the reel. When a fish is pulling the line too hard and you cannot raise your rod to keep the best angle, then you release the brake lever and send some line to the fish and raise your rod. The main line of nylon, 0.23 - 0.28 mm thickness, is spooled on the 2500 or 3000 size reel.
The float is very important in this fishing. It works not only as a bite indicator but also as a tool to adjust the drift of the rig. The bite indicator function is clear, when a fish bites and runs away the float moves, to let the angler realize the bite. Another function may not be so clear. In Iso Fukase, the float does not necessarily stay on the surface. Anglers adjust how it sinks by adding the split sinker, while selecting the best float in terms of suitable size to catch the current and buoyancy to control sinking speed. This is why there are many types of floats in Japanese fishing shops. At least, there are 5 to 6 levels of buoyancy, depending on brands, and hundreds of shapes. Even some floats are specialized for sinking to catch water current, that is a sinking float (very strange oxymoron.)
For hooks, the popular choice is Gure-shape hook.
It has a shorter shank, with a wide gape. It often has the circled hook point. The concept of this hook is that it is easy to get swallowed, but making sure to hook on the mouth. There are different wire thicknesses to make the best balance of strength and lightness. It is important to drift the hook with a bait as naturally as possible, and it is better to have a lighter hook if it holds the power of the fish. For the same reason, size selection tends to be smaller. Counterintuitively, even for the biggest Mejina, number 6 to 9 sizes are used, and for the average size fish sizes of 3 to 5 are used. Hook size bigger than 9 is for other targets of Iso Fukase, such as Hiramasa (Yellow amberjack) or Shima-aji (White trevally.)
For the bait and chumming, defrost krills are used. Often artificial powder baits are mixed with krills to make the chumming easier. These powders make it easy to treat krills, with adding dough or paste-like texture, for the best throwing distance, and also it can control how easy krills spread in the water.
Iso Fukase is all about the flow
The rocks on the water make the flow complicated. You need to understand how the water in front of you moves, to present the bait and chumming in front of Mejina.
Suppose you are on the shore, knowing that the mainstream is flowing from right to the left. Then the flow around you will be like small arrows with broken lines, in the below figure.
In some parts, the water flows out in an offshore direction. Other positions see the water flow against the rock. To make the situation more complex, you have to imagine the flow in 3D.
Can you think where to start chumming and where to place your rig, in the sea as shown in the picture below?
In this sea, the mainstream is flowing in the direction from left to right, 30 to 50 m offshore. There is flat water about 5 m away from you. It is the place where the water flows upward, and no small waves. There are swirls in front of you. In this part, water moves downward. These swirls are so strong that they create bubbles to make the water whitish. This whitish point may be nice for fish to hide and feel security.
In this fishing spot, you can throw chum and send your rig right in front of you. Then the chum and hooked bait sink, smoothly and rapidly, in the forward-right direction. If you want to fish more slowly, then you can fish more to the right, where there is no swirl.
If you can send your chumming and bait in good coordination, like the figure below, then it is highly likely that fish will bite your bait.
Iso Fukase fishing is done in the middle of the wild nature, while you are grasping the situation in front of you. You have to be a part of the surrounding environment to get the target fish. This is the reason why this traditional fishing has been shining as one of the favorite styles among Japanese anglers.

4 thoughts on “Pleasure of Iso Fukase Fishing”